Reconstruction of long-term dynamics of Chernobyl-derived 137Cs in the Upa River using bottom sediments in the Scheckino reservoir and semi-empirical modelling
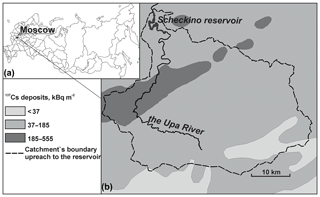
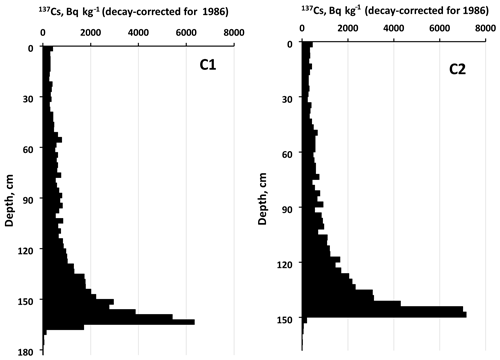
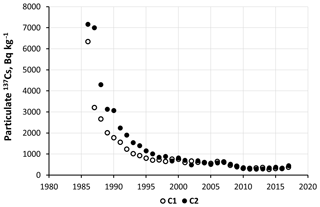
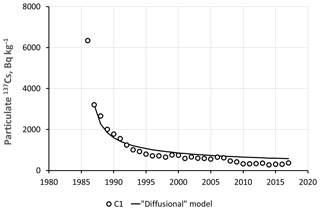
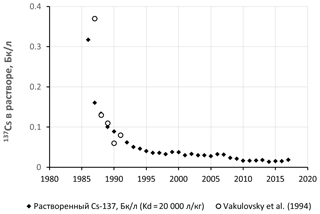
Two cores of bottom sediments were collected in 2018 to a depth of ∼200 cm in the deepest part of the Scheckino reservoir on the Upa River (9500 km2), Tula region, Russia. This area was severely contaminated by radiocesium (r-Cs) after the Chernobyl accident in 1986. The fact that 137Cs activity concentrations in a specific horizon of the bottom sediments correspond to 137Cs concentrations associated with suspended matter delivered to the reservoir, provides a basis for constructing the dynamics of particulate 137Cs activity concentrations in the Upa River catchment from 1986 to 2017. Over the time since the Chernobyl accident, the particulate 137Cs concentrations have decreased by more than an order of magnitude, with only minor changes occurring during the last 15 years. Using a typical value for the distribution coefficient Kd for the rivers of the Chernobyl contamination zone, dissolved 137Cs activity concentrations in the Upa River have been estimated and their changes over the past 30 years since the accident have been studied. The resulting estimates of dissolved 137Cs concentrations in the Upa River have been found to be in good agreement with measured data over the period 1987–1991. The proposed and tested method provides a basis for reconstructing the long-term dependence of radionuclide concentrations in rivers and reservoirs based on their vertical distribution in bottom sediments. Reconstructed time dependencies of particulate and dissolved 137Cs activity concentrations in the Upa River were found to be described well by the proposed semi-empirical “diffusion” model based on an assumption that the time dependency of particulate r-Cs in the river corresponds to the time dependency of its concentration in top soil layers across the catchment which can be approximated by a dispersion-convection equation with physically meaningful parameters.