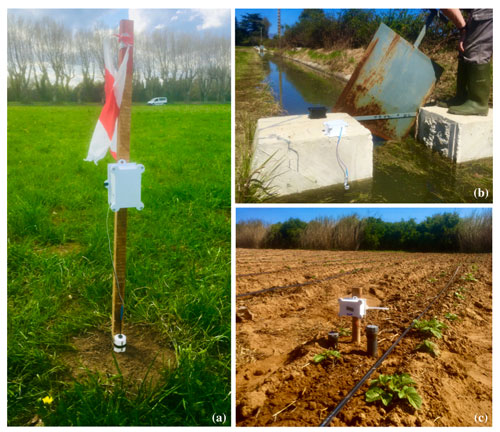
Exploring ways to improve agricultural water management in two Mediterranean irrigated systems: promises of wireless low-tech sensor networks
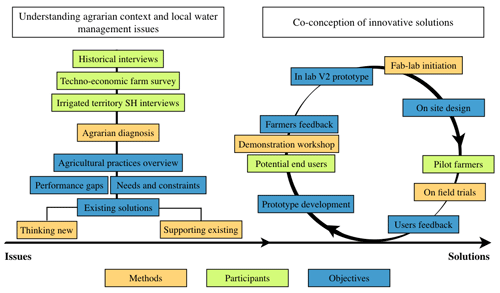
Unsustainable use of water resources and climate change will exacerbate the already existing tensions on resources, especially in the Mediterranean context. Despite investments in modern, economically and energetically costly equipment, the performance of irrigated agriculture remains below expectations, notably because of inappropriate irrigation practices, due to insufficient knowledge of irrigation actual need and limited use of decision support tools. Access to information at an unprecedented level, via easily accessible low-cost and low-tech sensors, may be a major lever for better identifying achievable performance gains, at different spatial and temporal scales, and for guiding stakeholders towards more sustainable practices. To explore this hypothesis, we have worked on the emergence of such technologies within two Mediterranean irrigated systems (Provence, France, and Cap Bon, Tunisia) facing major water use efficiency issues. Interviews were conducted on each site in order to identify main local needs and constraints that limit sustainable water management, and potential levers to improve irrigation performance. Innovative technological systems (water sensors, automation, Internet of Things networks) have been developed in response and tested in field through a participatory approach. The technologies were then designed to be low energy, low-tech and low-cost, based on the hypothesis that the lack of accessibility – investment and maintenance costs, system readability – of existing equipment was a brake to the dissemination of innovations in the agricultural sector. We believe that the adoption of such technologies could contribute to improve irrigated systems sustainability by playing on several dimensions: promote suitable and sparing water use by improving decision-making; help maintain agricultural production by decreasing input costs; improving water users' working conditions. Generally, accompanying the transition towards more sustainable practices, by providing to the stakeholders keys for better understanding of their system. The performance gains achievable with these innovations, heeding their inherent weaknesses (eg. lower robustness and accuracy), and the potential impacts of their adoption at a larger scale remain to be assessed in an integrated way.